Service
Respiratory Diseases
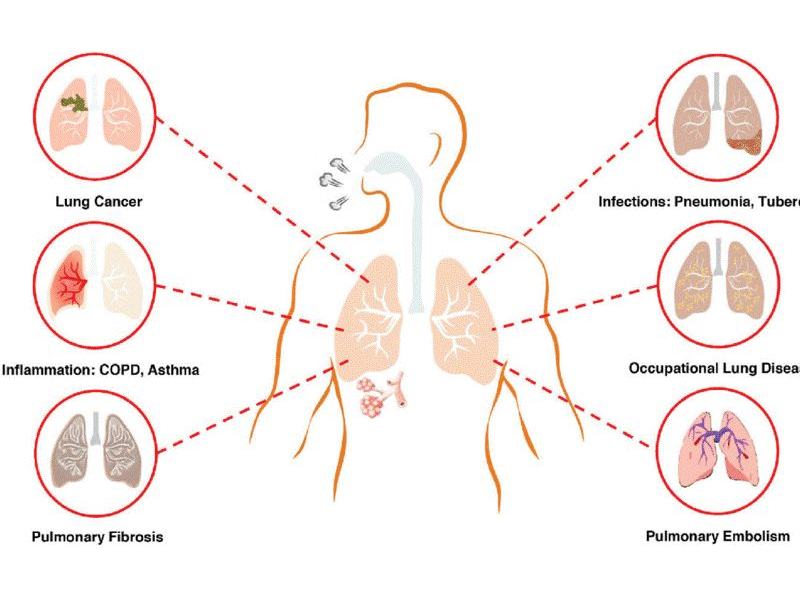
Respiratory diseases are illnesses that affect the lungs and other parts of the respiratory system, impacting the ability to breathe effectively. These diseases can be caused by infections, environmental factors, or genetic predispositions.
Common Respiratory Diseases
- Asthma : A chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways, causing recurring periods of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : A group of lung diseases that block airflow and make it difficult to breathe, often caused by smoking.
- Pneumonia : An infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup in the air sacs.
- Lung Cancer : A malignant tumor that develops in the lungs, often associated with smoking and exposure to pollutants.
- Tuberculosis : A bacterial infection that primarily affects the lungs, causing coughing, fever, and weight loss.
- Cystic Fibrosis : A genetic disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system, causing thick mucus buildup.
- Occupational Lung Diseases : Lung conditions caused by exposure to harmful substances in the workplace, such as asbestos, coal dust, or chemicals.
- Pulmonary Hypertension : High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs, which can lead to shortness of breath and fatigue.
- Pulmonary Edema : Abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs, often caused by heart failure or other medical conditions.
Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases
Symptoms can vary depending on the specific disease but may include
- Coughing (with or without mucus)
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Chest pain or tightness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Sputum production (mucus coughed up from the lungs)
Causes of Respiratory Diseases
- Infections : Viral or bacterial infections can lead to pneumonia, bronchitis, or other respiratory illnesses.
- Environmental Factors : Exposure to air pollution, tobacco smoke, occupational dusts, and other irritants can damage the lungs and increase the risk of respiratory diseases.
- Genetic Predisposition : Some respiratory diseases, like cystic fibrosis and asthma, can be inherited.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for respiratory diseases depends on the specific condition and its severity. It may involve
- Medications (bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, etc.)
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation (exercise and breathing techniques)
- Lifestyle changes (smoking cessation, avoiding irritants)
- Surgery (in some cases, such as lung cancer or severe COPD)
