Service
Blood Pressure (BP)
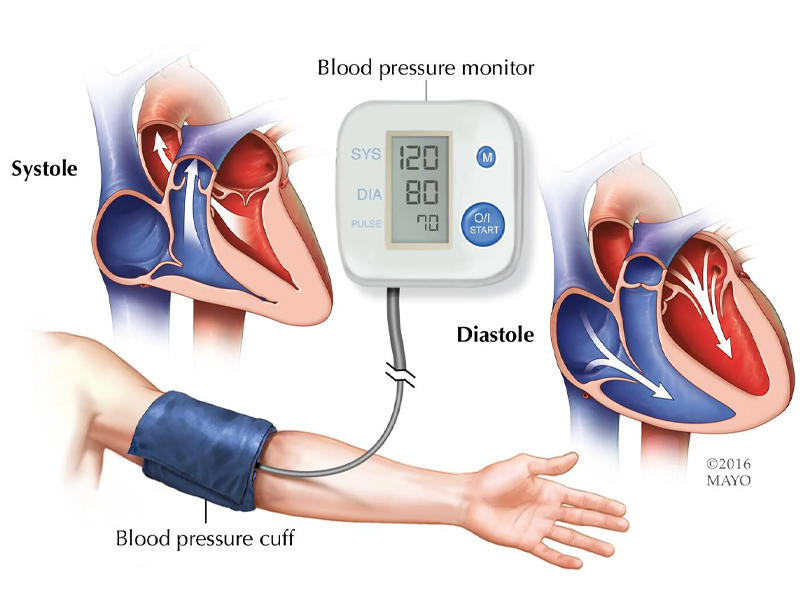
Blood pressure (BP) is the force of circulating blood against the walls of your arteries, and it's a crucial indicator of cardiovascular health. It's measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is typically presented as two numbers: systolic (pressure when the heart beats) over diastolic (pressure when the heart rests). High blood pressure, or hypertension, can lead to serious health problems like heart disease and stroke if left untreated.
What is Blood Pressure?
- Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels.
- It's primarily a result of the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system.
- The term "blood pressure" usually refers to the pressure in the brachial artery (the main artery in the upper arm).
Systolic pressure
The top number in a blood pressure reading, it represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood out.
Diastolic pressure
The bottom number, it represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart muscle is relaxed between beats.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
- High blood pressure significantly increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and other health issues.
- A reading of 130/80 mmHg or higher, most of the time, is considered high blood pressure.
- Elevated blood pressure (120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic) is also a warning sign.
What's a Healthy Blood Pressure?
- A healthy blood pressure reading is generally considered to be less than 120/80 mmHg.
- Normal blood pressure is typically considered to be between 120/80 mmHg and 129/84 mmHg.
- High normal blood pressure is between 130/85 mmHg and 139/89 mmHg.
Managing Blood Pressure
- Lifestyle changes, such as diet, exercise, weight management, stress reduction, and quitting smoking, can help manage blood pressure.
- If lifestyle changes aren't enough, medication may be necessary to lower blood pressure.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
