Service
Pneumonia
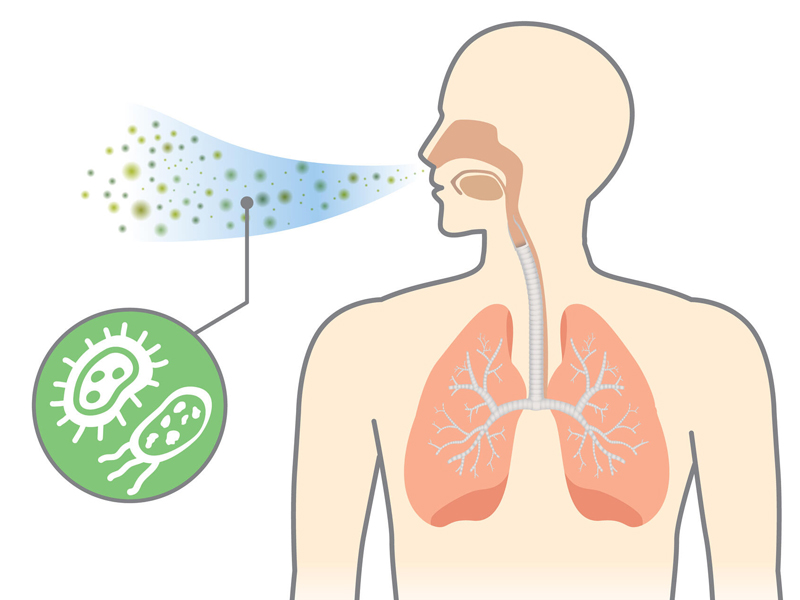
Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs, specifically the air sacs (alveoli), which can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It leads to inflammation and fluid or pus buildup in the lungs, making breathing painful and difficult. Symptoms range from mild to severe and can include cough, fever, chills, and shortness of breath.
What is it? Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, causing a variety of symptoms.
- Causes : Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Bacterial pneumonia is the most common type and can sometimes develop after a viral infection like a cold or the flu.
- Symptoms : Common symptoms include cough (sometimes with mucus), fever, chills, and shortness of breath. Older adults may also experience confusion or a lower-than-usual body temperature.
- Severity : The severity of pneumonia varies, with some cases being mild and others requiring hospitalization. Factors like the cause of the infection, age, and overall health influence the severity.
- Risk factors : Infants and young children, adults 65 and older, and people with chronic health conditions or weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
- Diagnosis : Diagnosis typically involves a medical history review, physical exam, and possibly chest X-rays or other tests.
- Treatment : Treatment depends on the type and severity of pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia is usually treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may not require specific treatment. Oxygen therapy and other supportive measures may also be needed.
- Prevention : Vaccines can help prevent some types of pneumonia, and good hygiene practices can also reduce the risk.
